SWOT Analysis: Strategic Planning
What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning method that helps evaluate a business's internal and external environment. The acronym stands for four components:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
Internal Factors (Controllable by the Company)
Strengths
Internal advantages of your business:
- Unique competencies and team expertise
- Strong brand and market reputation
- Financial stability and profitability
- Skilled staff with low turnover
- Efficient business processes and operational model
- Innovative products or technologies
- Loyal customer base with high LTV
Weaknesses
Internal shortcomings that need addressing:
- Limited resources (finances, people, time)
- Outdated equipment or technical debt
- Weak presence in certain market segments
- Lack of qualified personnel in key roles
- Inefficient processes and bureaucracy
- High operating costs
External Factors (Uncontrollable)
Opportunities
Favorable external factors:
- Growing market or new niches
- Legislative changes in your favor
- New technologies for automation
- Weakening of major competitors
- Shifts in consumer preferences in your favor
- Opportunities for strategic partnerships
Threats
Potential business risks:
- Increased competition and new entrants
- Economic downturn or crisis
- Changes in industry regulations
- Shifts in consumer demand
- Technological disruptions
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis Step by Step
- Preparation: Assemble a cross-functional team (5-7 people)
- Brainstorming: Each participant writes ideas for each quadrant (15-20 min)
- Prioritization: Keep 5-7 most critical factors in each category
- Interconnection Analysis: Create a strategy matrix (SO, WO, ST, WT)
- Action Plan Development: Formulate specific actions with assignees and deadlines
SWOT Strategy Matrix
- SO Strategies: Leverage strengths to capitalize on opportunities
- WO Strategies: Overcome weaknesses by exploiting opportunities
- ST Strategies: Use strengths to mitigate threats
- WT Strategies: Minimize weaknesses and avoid threats
Practical Case: City Center Coffee Shop Analysis
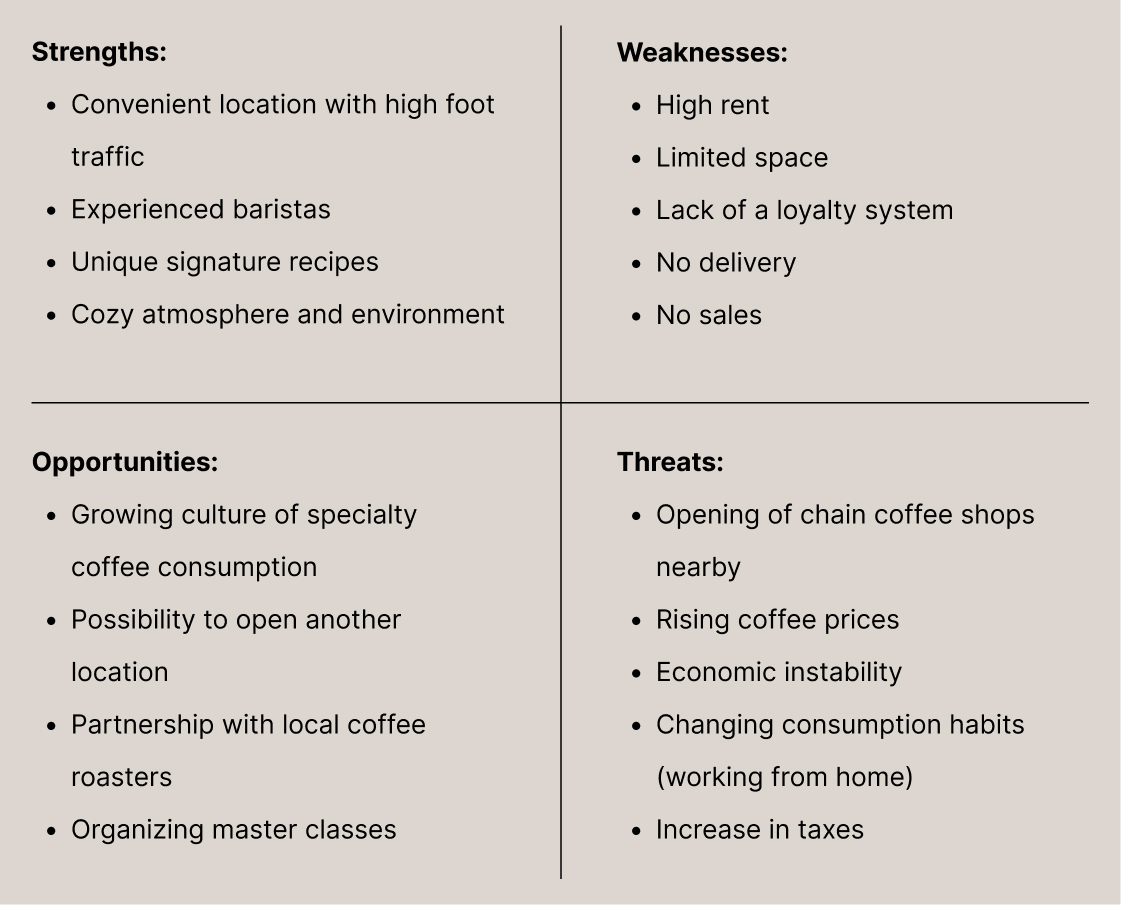
Coffee shop SWOT analysis: from evaluation to strategy